Digital X-Ray
X-Ray is a form of invisible, high-frequency electromagnetic radiation which a very small and energetic. They are produced by accelerating electrons at a metal target. X-Rays are used in various medical applications, especially for imaging.
Today, different types of X-Rays are used for specific purposes. For example, mammograms are used to examine the breasts and a barium enema is used to detect bowel problems.
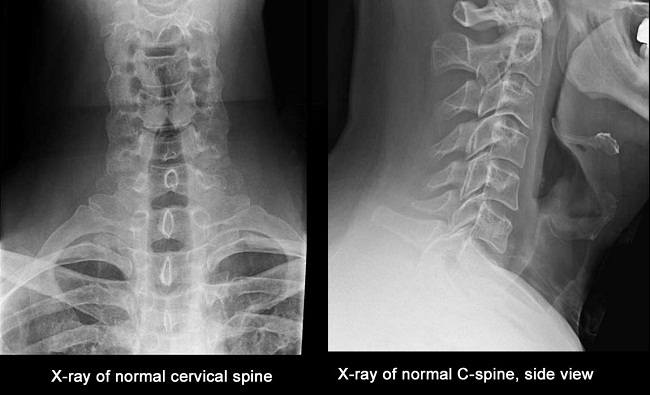
Bone is a very hard and dense tissue that shows up clearly on X-Rays. X-Rays are therefore very useful for diagnosing bone-related problems.
For example, X-Rays can be used to help identify:
Fractures and breaks
Problems with teeth, such as tooth decay
Thinning and weakening of the bones (Osteoporosis)
Bone infection (Osteomyelitis)
An abnormal curvature of the spine (Scoliosis)
Bone Cancers, such as osteosarcoma and Ewing’s sarcoma
X-Rays are also sometimes used during investigative or therapeutic procedures to help the surgeon guide equipment to the area being examined or treated.
CHEST EXAMINATION
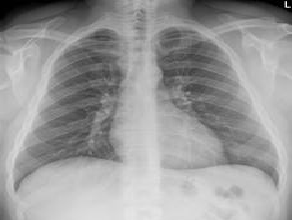
Although major organs and blood vessels do not show up as clearly on X-Rays as bones, they are visible. A chest X-Ray is therefore a good way of identifying changes or abnormalities in your heart, lungs and major arteries.
TYPES OF X-RAY
Barium is a type of contrast medium that you may be given in a solution to drink. After the barium has moved down into your upper digestive system, a series of X-Rays will be taken. A barium swallow can be used to diagnose problems with the upper digestive system, such as swallowing problems (Dysphagia) and persistent symptoms of abdominal pain.
A barium enema involves barium solution being pumped through your anus (Back passage) and into your bowel. Barium enemas can be used to diagnose bowel problems, such as persistent constipation and blood in your faeces (Stools).
During an intravenous urogram (IVU), contrast medium is injected into your veins. Iodine solution is usually used, which moves into your kidneys and bladder. X-Rays of your kidneys and bladder will then be taken. IVU is often used to diagnose urinary system problems.
WHY X-RAY?
An X-Ray machine is used to take pictures of dense structures in the body. The machine uses photons that pass through the body. Very dense structures, such as bones, do not allow the photons to pass through and will appear white. Air appears black, and fluid, fat and muscles will appear as shades of gray. X-Ray machines are used extensively in the health care industry. The resulting X-Ray pictures are called radiographs.
Computed Radiography
Computed Radiography , uses very similar equipment to conventional radiography except that in place of a film to create the image, an imaging plate (IP) made of photostimulable phosphor is used. The imaging plate is housed in a special cassette and placed under the body part or object to be examined and the x-ray exposure is made. Hence, instead of taking an exposed film into a darkroom for developing in chemical tanks or an automatic film processor, the imaging plate is run through a special laser scanner, or CR reader, that reads and digitizes the image. The digital image can then be viewed and enhanced using software that has functions very similar to other conventional digital image-processing software, such as contrast, brightness, filtration and zoom.


No silver based film or chemicals are required to process film.
Reduced film storage costs because images can be stored digitally.
Computed radiography often requires fewer retakes due to under- or over-exposure which can result in lower overall dose to the patient, if you assume a moderate amount of retakes. CR can require up to 30% less dose than film.
Image acquisition is much faster – image previews can be available in less than 10 seconds.
By adjusting image brightness and/or contrast, a wide range of thicknesses may be examined in one exposure, unlike conventional film based radiography, which may require a different exposure or multiple film speeds in one exposure to cover wide thickness range in a component.
Images can be enhanced digitally to aid in interpretation.
Images can be stored on disk or transmitted for off-site review.
Satyakiran Healthcare 2017. Powered by Exact IT Solutions Pvt. Ltd.




